Browse
During my residency in Taipei, I have been looking for archives and references on the connection of Indonesia and Taiwan, both historically and contemporary. This search had brought me to museums and libraries. I’ve been flipping through books about the Dutch and Japan colonial regime in Taiwan while tried to compare it with the colonial time of Indonesia. Though the archives and references on Taiwan-Indonesia connection are not only stored in library and museum. The narrations of the two regions’ relation are embedded, yet also fragmented, in the city landscape and its inhabitants. In this regard, I have developed interest on the Taipei’s New Park (or what’s known now as 228 Memorial Park) because of its historical and political significance which spans through different regimes in Taiwan up until now.
The park was the location for Taiwan Expo, a colonial exhibition in 1935, and now it is the place protest for indigenous group to demand their land rights, a cruising area, and site for other forms of congregations which are benefited from its location in the city center yet open for public usage with certain boundaries. Based on my research, I’m creating an audio guide of the New Park / 228 Memorial Park to unravel the layers of narrations upon the public space with three voices of narrators; a student, worker, and visitor. These narrators represent various subjects which I had encountered, in person and through text, during my stay in Taiwan. It is also the overlook positions in the discourse of citizenship and historiography. A migrant worker who thinks constantly about home, a foreign student who doesn’t feel like she belongs anywhere, an indigenous community member who was forced to travel to see the light of civilization in the city. Their biographies are intersecting in place yet apart in time. Through these narrators and the audio guide on the New Park / 228 Memorial Park, I would like to propose a way of imagining worldview from listening to personal narratives of the displaced.
Nusantara and the Project of Decolonization
As someone who grew up and being educated in Java Island (specifically Jogja and Jakarta) where unfortunately being Javanese means being Indonesian, I would immediately associate the term Nusantara with Gadjah Mada’s oath, Sumpah Palapa. Gadjah Mada is the maha patih (prime minister) of Majapahit Empire (1293-1527), an empire which was centered in Java island with its areas of power cover the nowadays Southeast Asia. In this oath, Gadjah Mada, the maha patih (prime minister) of Majapahit Empire declared that he will not eat Palapa fruit until he succeed in conquering the Nusantara.
I remember back in my elementary to junior high school time (1994-2003), the students will have to memorize the oath of Gadjah Mada. Yet in the Bahasa Indonesia version which we all need to memorize as student, Gadjah Mada’s will is to unite (menyatukan) instead of conquering (menaklukan) Nusantara. Gadjah Mada is the national hero who brings the idea of unity across Nusantara archipelago. At school, we memorized Gadjah Mada’s oath and Majapahit as the shared history of Southeast Asia people. It’s what brings us together, unite us.
Yet the entanglement of the notion of Nusantara with the history of conquest is something that remains hidden. Pramoedya Ananta Toer had mentioned in his historical novel, Arus Balik, on how Gadjah Mada was able to conquer Nusantara under Majapahit Empire, with muskets in only 20 years. After the fall of Majapahit Empire in 1527, Nusantara was divided into smaller kingdoms with constant encounters with actors from foreign lands including China, Arab, and Europe. Then the conflicts with Portuguese, Spaniards were escalated, especially due to the attempt to monopolize the spice trade and market, until Dutch East India Company had taken its hold upon Indonesia archipelago started from 1603.
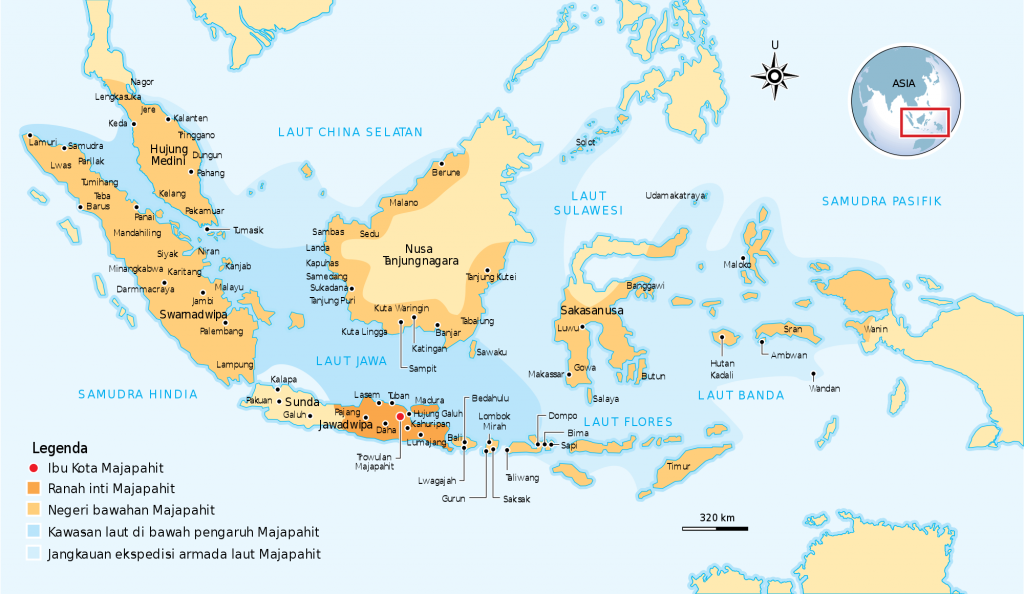
Nusantara is not only about shared history of an archipelago, of Southeast Asia. It’s a notion of worldview which was used along with the attempt to conquest, dominate, in order to enforce power upon others, especially as means for accumulation of wealth.
Later in 20th century, Gajah Mada’s name is being immortalized as the one of the first university in Indonesia, Gadjah Mada University, located in Jogja. In 1976, an Indonesian telecommunication company launched Palapa, a series of communication satellites on a US rocket from Kennedy Space Center, in Florida. President Soeharto, the president of Indonesia at that time of New Order Regime, deliberately choose Palapa as the satellite name, from the Palapa oath of Gajah Mada, with the intention to show Indonesia’s glorious past and hope that the system can unite the archipelago.
Nusantara, as perhaps like many other notions of worldview, can be dangerous when it’s being utilized as means of conquest, domination, or specifically for the expansion of market under the pretext of shared history and / or identity . On the other hand, the understanding of shared history across regions might also allow us to do a comparative study on today’s problems, such as forced migrations, exploitations of labour, enclosure of resources, and compose the so-called our shared struggle for collaborative survival. This is a call for a project of decolonization, through unravel the past, reflect on our present and imagine the possible future.
It is a call for alternative worldview.